September is Gynaecological Cancer Awareness Month
80% of ovarian cancer occurs in women over 50
Gynaecological cancer refers to the five cancers that start in a woman’s reproductive system – cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, vaginal cancer, vulval cancer and womb cancer (also known as endometrial or uterine cancer).
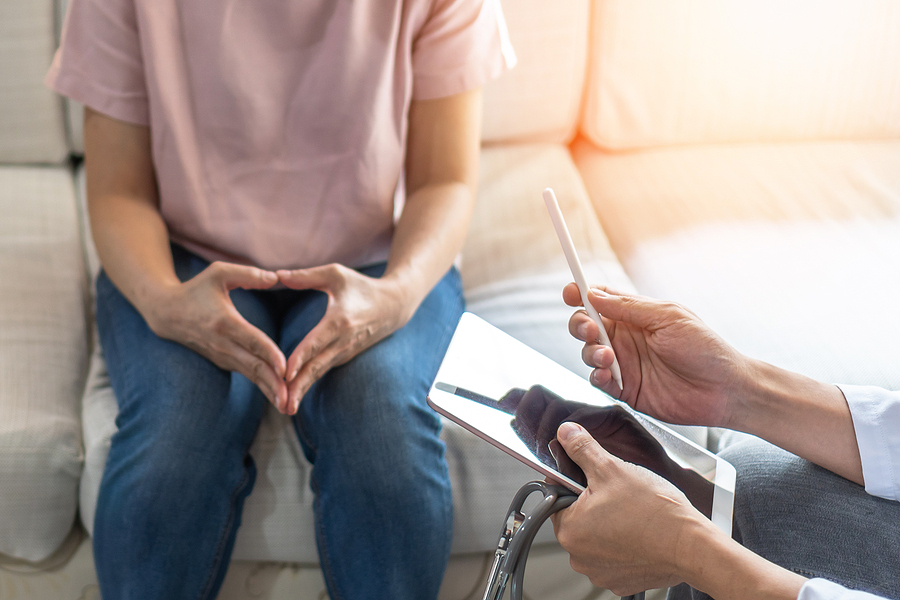
September is Gynaecological Cancer Awareness Month and is used as an opportunity to encourage women to become more aware of these cancers including early detection and prevention.
21,000 women are diagnosed with gynaecological cancer every year in the UK. Every single day 58 women are given this life-changing news and sadly, each day, 21 women will die from their gynaecological cancer.
“The problem is that many women are still not confident in spotting the symptoms of gynaecological cancer and therefore they don’t seek help until the disease has spread which makes it harder to treat.” Mr Simon Butler-Manuel, GRACE Charity Founder
In order to recognise the signs and symptoms of gynae cancers and raise awareness, it may be helpful to understand a little about what these cancers are.
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a term that encompasses gynaecological cancer located in the ovaries, tubes and peritoneum. About 7,500 women are diagnosed with ovarian cancer each year and 80% of ovarian cancer occurs in women over 50. Ovarian cancer doesn’t always cause symptoms, or if it does, they might seem vague or similar to other conditions. If you experience the below symptoms and they are unusual for your body or don’t go away, let your doctor know.
Symptoms can include:
• Abdominal bloating or swelling – which is persistent and doesn’t come and go
• Loss of appetite, difficulty eating and feeling full more quickly
• Abdominal or pelvic pain felt over a period of time
• A change in bladder habits
Vaginal bleeding or pain during intercourse may sometimes occur and although these symptoms are common to many other conditions the development of new abdominal symptoms in a middle-aged woman is always a concern and should be investigated.
Endometrial Cancer
There are two main types of uterine cancer: endometrial cancer, which occurs in the lining of the uterus, and uterine sarcomas. Endometrial cancer is the 4th most common cancer. It is most prevalent in post-menopausal women, although 20% of cases present in women of childbearing age. About 9,000 new cases are diagnosed each year in the UK and approximately 2200 of these women will die of the disease.
Symptoms can include:
• Post menopausal bleeding
• Bleeding between periods or heavier than normal periods
• A watery or blood-stained discharge
There is no proven screening test for uterine cancer, so it’s important that you let your doctor know if you notice any changes, particularly a change in discharge.
Vaginal Cancer
Cancer of the vagina is one of the rarest forms of gynaecological cancer with fewer than 300 women diagnosed each year in the UK, and just over 100 women dying of the disease. It tends to mostly affect older women, with 70 being the average age of diagnosis, but it can affect women of any age.
Symptoms can include:
• A blood-stained vaginal discharge
• Bleeding after sexual intercourse and pain
• Blood in the urine, the need to pass urine frequently and the need to pass urine at night
• Pain in the back passage (rectum) may occur
Vulval Cancer
Vulval cancer (also known as vulvar cancer or cancer of the vulva) is cancer that occurs on the genitals on the outside of a woman’s body. This includes the labia minora and labia majora, the clitoris, the pubic mound and the perineum, which is the skin between the vagina and anus. Vulval cancer is more common in women who have gone through menopause, but it can affect women at any age. These cancers usually present with an itchy or painful skin lesion, wart-like growth or ulcer on the genital skin. There are about 1,300 a year in the UK, 460 of these women will die of the disease.
Symptoms can include:
• Persistent itching, burning or soreness of the vulva
• Bleeding or a blood-stained discharge
• Pain in the area of the vulva
• A lump or swelling over the vulva
• A burning sensation on passing urine
• A mole that changes shape or colour
The risk of developing this cancer increases with age. Other risks factors include HPV infection, weakened immune system, genital herpes infection, smoking and some chronic skin infections.
Cervical Cancer
This cancer is the most common cancer in women under the age of 35. However, the good news is that cervical cancer is one of the most preventable types of cancer. Almost all cervical cancers are caused by HPV infection and so preventing HPV can also prevent cervical cancer. Thanks to the success of the UK screening and vaccination programmes it is being detected earlier. However, incidences will rise as only 75% of women take up screening and HPV vaccination. The risk of cervical cancer is doubled if you smoke.
Symptoms can include:
• Vaginal bleeding between periods
• Bleeding after sexual intercourse and pain
• Vaginal bleeding after the menopause
• A smelly vaginal discharge
While there are screening tests for some gynaecological cancers, for others there is no proven screening method. This means that it’s important for women to be aware of the possible signs and symptoms of gynaecological cancers and get to know their bodies well, so they can tell if anything changes
Significant amounts of information are available online about this awareness month and we encourage you to get informed and share your knowledge.
Melina - Assistant Editor
Latest posts by Melina - Assistant Editor (see all)
- Cream Cheese Orange Bars - May 2, 2024
- Top tips for hay fever sufferers - April 14, 2024
- Paysan Breton Cream Cheese Breakfast Wraps - April 12, 2024
- 4 Homemade Sweet Treats for Easter - March 24, 2024
- Playground Memories - March 10, 2024