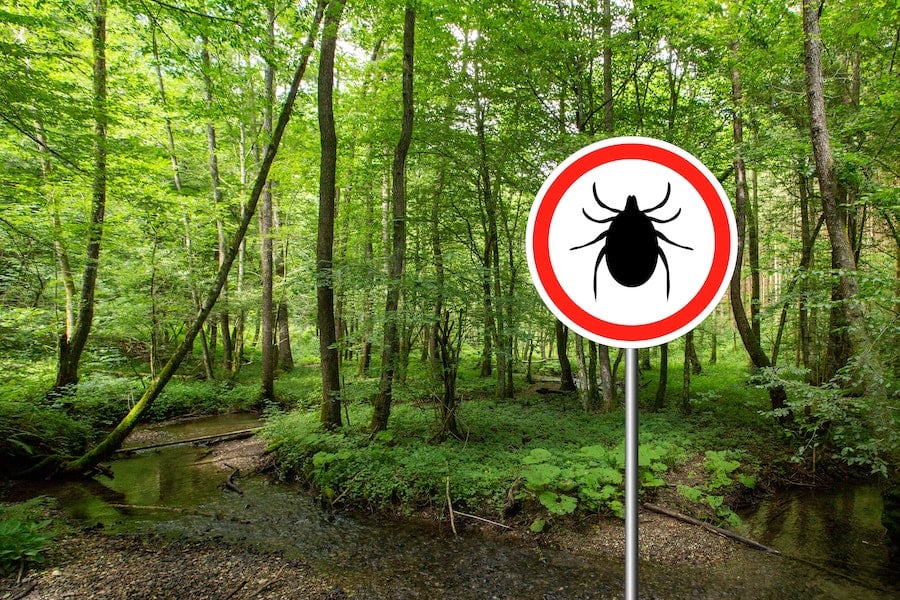
9 things a Lyme disease expert wants everyone to know
Lyme disease is on the rise across the UK and globally, yet many people believe they’re unlikely to be at risk – or don’t really know what it means.
Experts are warning, however, that we could be just as likely to get bitten by an infected tick whether weeding in the garden or hiking in the countryside. They can be carried indoors by pet cats and dogs at time of year too.
Catching and treating Lyme disease early is vital, or symptoms can become chronic and very hard to manage – yet awareness is still low even among many doctors.
Here – ahead of the Calling Time on Lyme conference in London on November 16 – Dr Joshua Berkowitz, medical director and founder of the Lyme Disease Clinic UK (lymediseaseclinic.co.uk), outlines nine things he thinks everyone should know…
1. Hard-to-treat symptoms
“Lyme disease is a challenging condition to treat. After a tick bite, the bacterium moves very quickly through the body and is highly resistant to the immune system. Symptoms can be flu-like, fatigue, joint pain, headaches, fever, swollen lymph nodes, heart palpitations, neurological shakes and weakness. Some also experience memory loss, mental confusion, anxiety, depression and panic attacks. Keeping alert to odd descriptions or combinations of symptoms from patients and keeping Lyme disease in mind could help doctors pick it up more quickly.”
2. Misdiagnosis is common
“Lyme disease is known as the great imitator because its symptoms are so varied – even from patient to patient – and can be similar to other illnesses, such as fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, and also illnesses like depression or flu. The risk of misdiagnosis is that if someone is treated for another disease – for example, prescribed steroids for MS – that can exacerbate Lyme disease symptoms. Accurate diagnosis of Lyme disease is therefore a priority.”
3. Cases are increasing
“The NHS estimates there are now 3,000 Lyme disease cases diagnosed annually in the UK, although support groups believe the figure is much higher, with reports in 2019 already estimating approximately 9,000 new cases. The disease infects between 650,000 and 850,000 Europeans every year, and cases have quadrupled in the last 12 years around the world. The number of cases in the UK is predicted to rise annually as the disease becomes more prevalent across Europe, with warmer weather attributed to climate change providing the ideal environment for ticks.”
4. False negative blood tests confuse people
“There’s a very small window of time, between around 10 days and six weeks, when a blood test is likely to be accurate for diagnosing Lyme disease. At this early stage of the disease, the first line of attack – IgM immunoglobulins, which the immune system produces to fight the infection – will be detectable. After two or three months, the second line of attack, IgG immunoglobulins, will be active and the antibodies they create to defend the body against more persistent infection will be detectable. If a blood test is done too soon after infection, the IgM may not show up, hence the timing of a blood test is crucial for the most reliable outcome.”
5. It’s only curable if caught early
“Lyme disease can be cured if it’s caught early and treated aggressively with antibiotics. But if it isn’t caught early enough, the Lyme disease will become established in the body and the patient will suffer from the chronic form of the disease. Once chronic Lyme disease has taken hold, specialist treatments can help ease the symptoms and people can enjoy periods of remission, but relapses are common. There’s now a growing awareness that chronic Lyme disease exists and experts are working to improve the speed and quality of diagnosis and find successful treatments. A barrier lies in the way chronic Lyme disease isn’t yet fully recognised by the medical profession.”
6. Ticks aren’t just an outdoor/summer problem
“Ticks survive cold weather and you may be bitten in the winter. In addition, if your dog or cat has ticks, they can transfer to you, so checking pets is very important and killing and disposing of the tick correctly is essential.”
7. Ticks don’t just carry Lyme disease

Feeding time: A tick on human skin
“Lyme Disease is debilitating enough. Even worse, most ticks carry four to six other diseases. They are said to have a ‘dirty mouth’ as they carry many bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoans which they transmit in a single bite. In effect, when they bite you, all the bacteria they’re carrying from the blood of previous organisms they’ve bitten (including deer, squirrels, rats, dogs and cats) goes into your bloodstream causing co-infections.”
8. Not everyone gets a rash

Lyme disease sometimes causes a telltale circular rash
“The classic Lyme disease ‘bullseye rash is’ only experienced by around one-in-four people. Having this rash is a strong indicator you’re infected, but not having the rash doesn’t mean you’re in the clear. If you’ve been bitten by a tick/had to remove a tick from your skin, you’re at risk of infection and should see your GP straight away for a course of antibiotics. In addition, GPs must consider the possibility that a patient presenting with certain symptoms may well have Lyme disease – weeks or even months after potentially being exposed to a tick bite.”
9. Everybody is potentially at risk
“People still think Lyme disease-carrying ticks are mainly found in Europe, South America and the far reaches of Scotland. But that’s simply not true – ticks are everywhere – in woodlands, city parks, your front garden. You’re as likely to be bitten by a tick while weeding your garden as when hiking in the Scottish highlands. The UK must wake up to this fact – if you suspect Lyme disease, go to your GP and explain – don’t be fobbed off.”
The Press Association
Latest posts by The Press Association (see all)
- How to attract more bees to your garden - May 3, 2024
- The costly insurance pitfalls to avoid when kitting out your garden this summer - May 3, 2024
- Gavin And Stacey’s best moments: From Smithy’s Indian takeaway to Pam eating ham - May 3, 2024
- Princess Charlotte ‘s ninth birthday marked by picture release - May 2, 2024
- Strong passwords more important than ever, experts warn - May 2, 2024